- Home
- Infographics
- Falling film chiller
Falling film chiller
What is a falling film chiller?
This unit is a heat exchanger that is engineered to reach the desired temperature for cooling water; the cold water is used to cool down large amounts of this fluid in short periods of time and is also suitable for cooling contaminated liquids.
A falling film chiller can recycle water and decreases the plates temperature to optimal
levels; this recirculating falling film chiller will continuously cool down all fluids and keep
their temperature uniformly.
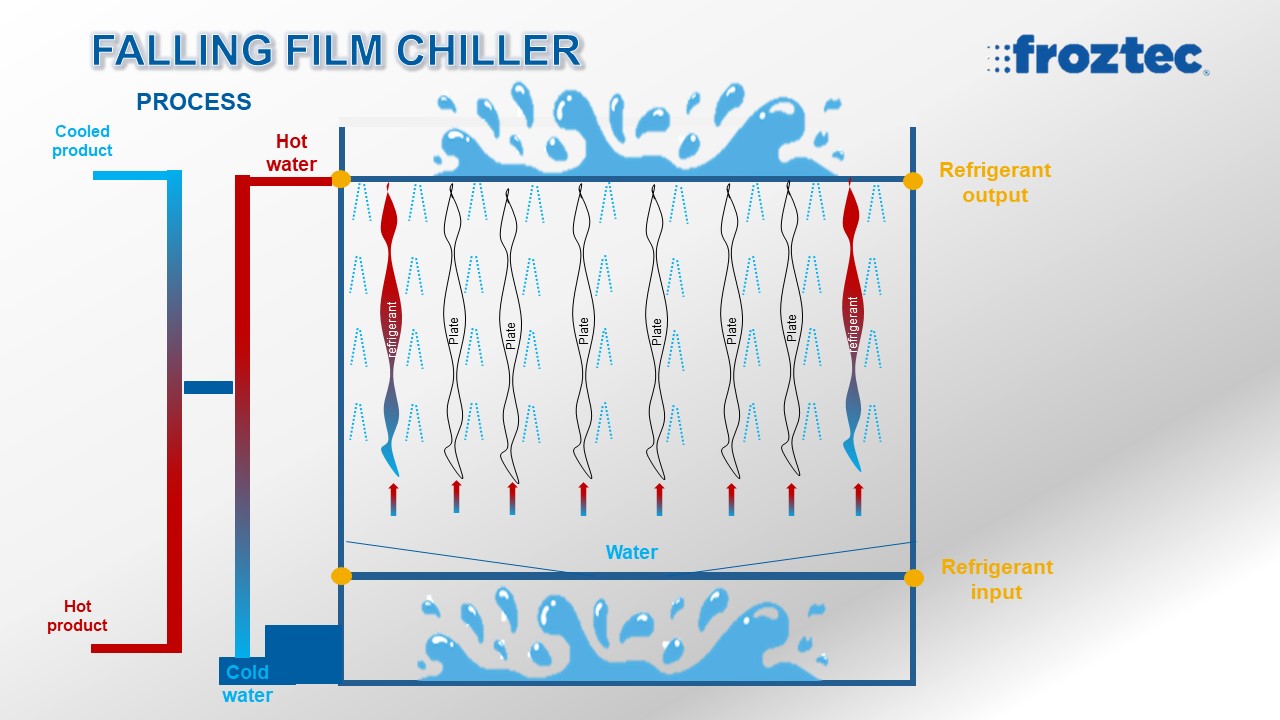
How does a falling film chiller work?
There is a water distribution tray at the bottom of this equipment with multiple orifices on its surface to drain water out of the tray and into the double-relief/double-pane laser plates hanging at the bottom.
A thin water layer falls on the plate and is cooled down to the desired temperature; the falling film chiller can cool water down to a temperature of 0.5 °C.
After cooling, cooled water travels from the plates and enters an optional tank where it is pumped and distributed to the next process, which could be another heat exchanger, a process tank or a food product; used water can be collected in a deposit and pumped back to the top part of the falling film chiller where the process starts all over again.
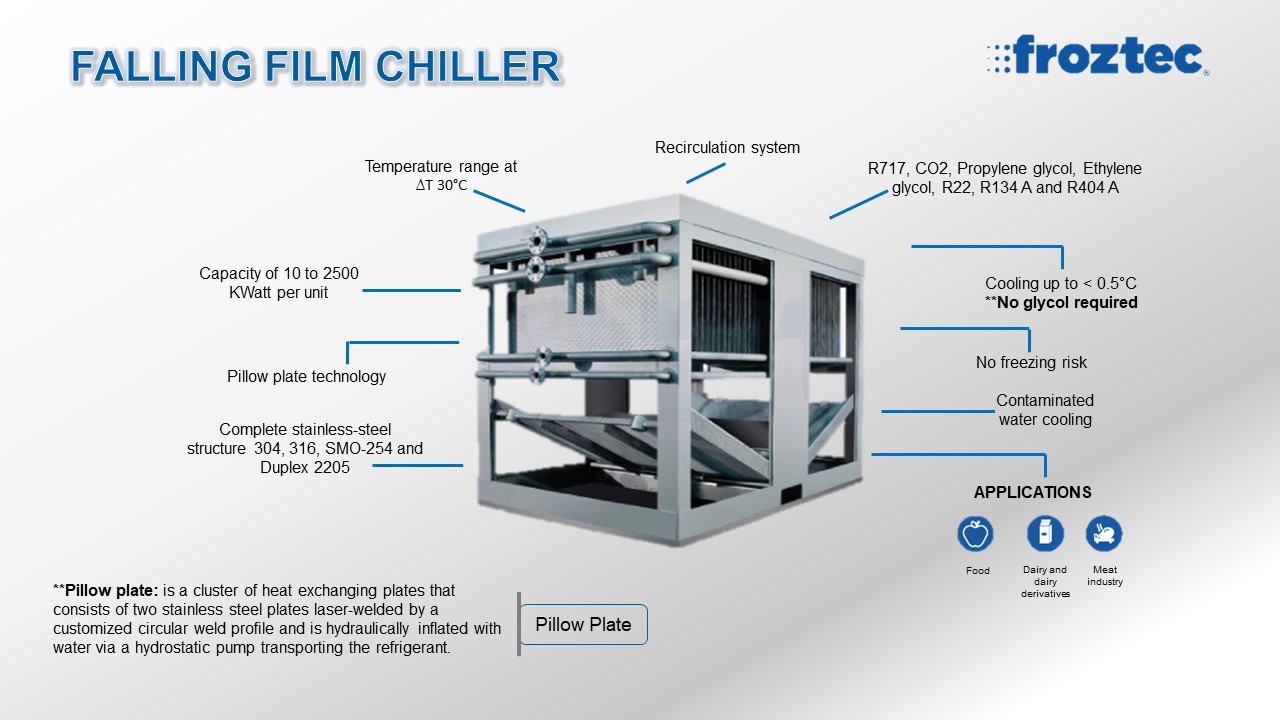
The Pilow Plate is a cluster of heat exchanging plates that consists of two stainless stee plates welded by a customized circular weld profile and is hydraulically inflated via a hydrostatic pump transporting the refrigerant.
Basic information for a proper selection
- Input temperature
- Output temperature
- Flow
- Cooling capacity
- Type of refrigerant
Benefits
- Efficient cooling in low temperatures (0.5°C) with no freezing risk.
- Consistent cooled water temperature.
- Open build-up for simple maintenance,
accessible for high-pressure cleaning. - Complete stainless-steel structure.
- Capable of cooling slightly contaminated water (particles of less than 5/16”).
APPLICATIONS
The falling film chiller is considered the best option for processes requiring cooling
down large amounts of fluids.
- Food industry
- Poultry industry
- Dairy and dairy derivatives cooling
- Meat industry