- Home
- Infographics
- Evaporative condenser
Evaporative condenser
What is and how does an evaporative condenser work?
This refrigeration equipment is used when the main form of energy, heat, from a cooling system fails to be harnessed during a process; therefore, the unit’s heat dissipation stage is performed by discharging any resulting water vapor
.
These units are engineered with the same principle as cooling towers, where the working fluid inside the cooling equipment is subjected to a process resulting in heat exchange, which is performed when the cooling fluid flow enters a tube bundle.
These units are engineered with the same principle as cooling towers, where the working fluid inside the cooling equipment is subjected to a process resulting in heat exchange, which is performed when the cooling fluid flow enters a tube bundle.
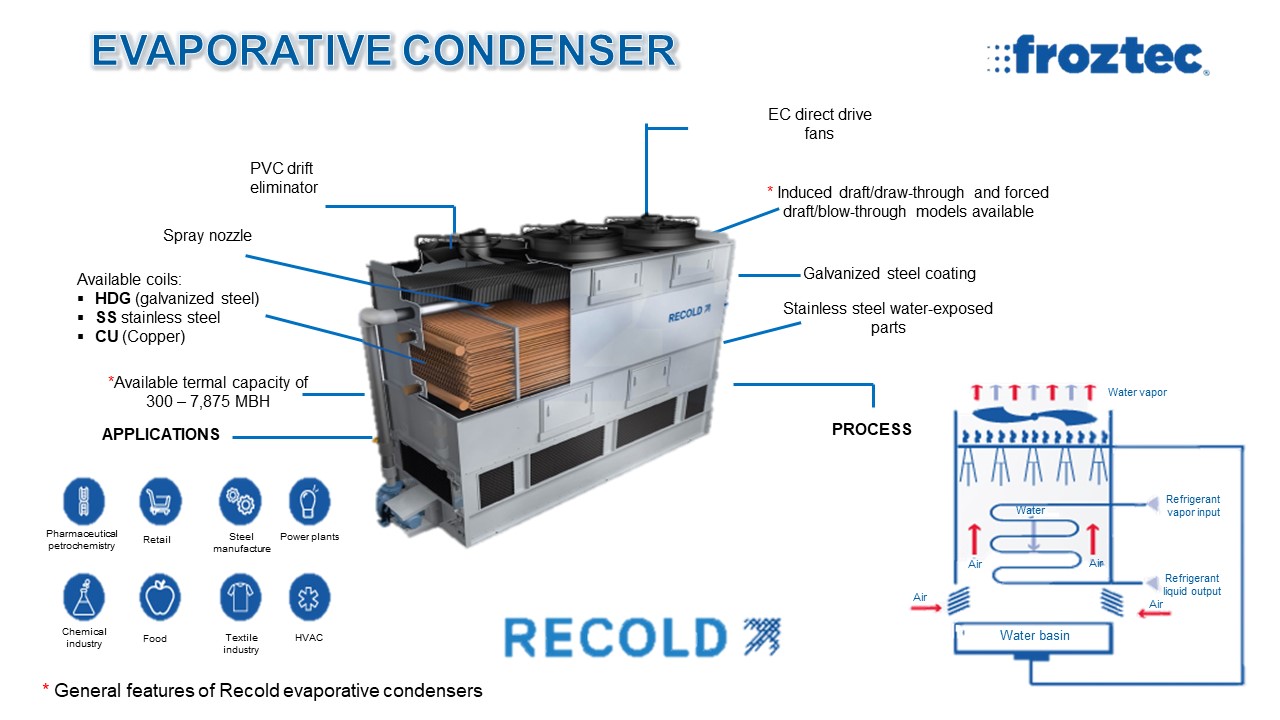
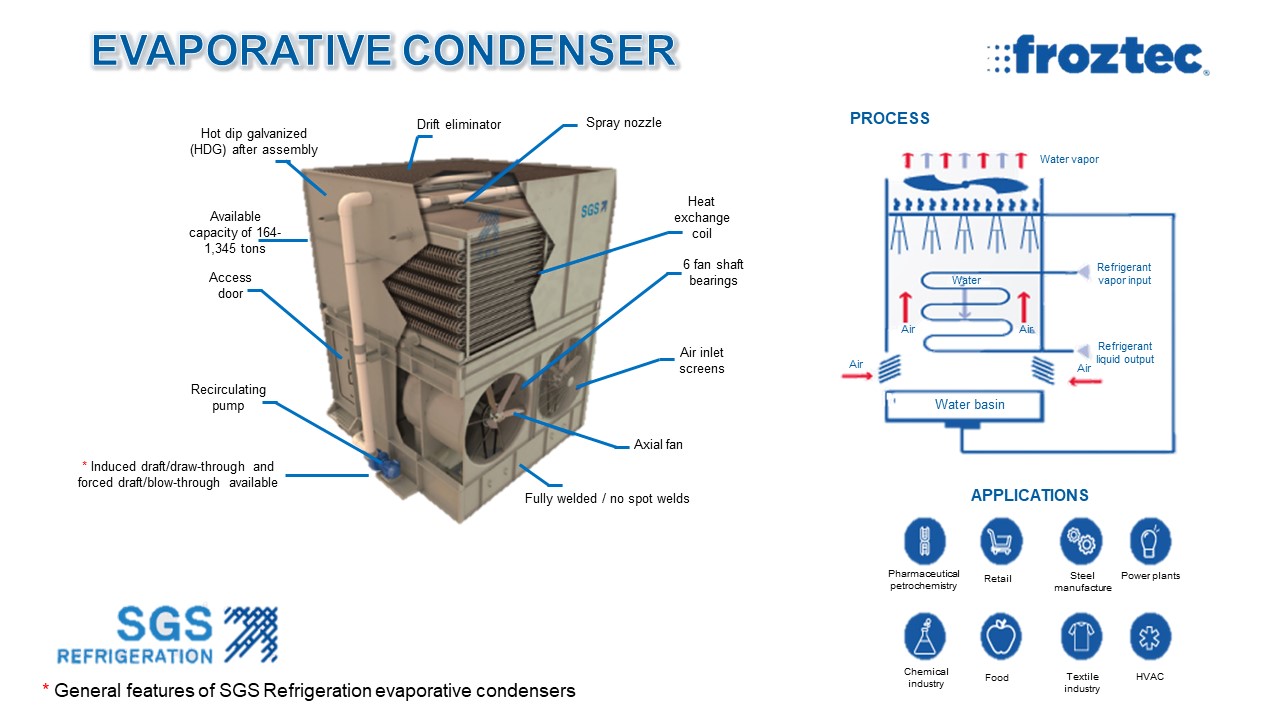
EVAPORATIVE CONDENSER OPERATION
- Refrigerant vapor travels to the heat transfer coil, where heat is dissipated, condensing this process fluid to liquid.
- After recirculating water is pumped from the collection basin to the pressurized distribution system, the coils will then distribute it to the next stage of the process.
- Heat is transferred from the refrigerant as the recirculating water flows over the outside of the coil tubes and into the fill media under the coil.
- The induced air from the condenser evaporates a small portion of the recirculating water, rejecting heat to the atmosphere.
BENEFITS.
- Single-piece installation
- Factory-installed controls
- Multiple access doors
- Copper (corrosion-resistant) or stainless steel coil
- High-efficiency, low sound levels
- Longer equipment service life
- Greater thermal efficiency
- More corrosion-resistant
- Lighter weight
- Electronically commuted fan motors
- Integral speed controls
APPLICATIONS.
- Retail
- Facilities climatization
- Petrochemical and Pharmaceutical industries
- Food industry
- Automotive industry
- Steel manufacture
- Electronic components manufacture
- Power plants
- Chemical industry
- Plastics industry
- Textile industry