- Home
- Infographics
- Fluid cooler
Fluid cooler
What is and how does a fluid cooler work?
Not only are these closed-circuit coolers capable of keeping the entire system clean and free of contamination but they are also considered the best option to use as climatization for the process industry in need of fluid-cooling systems.
Operation
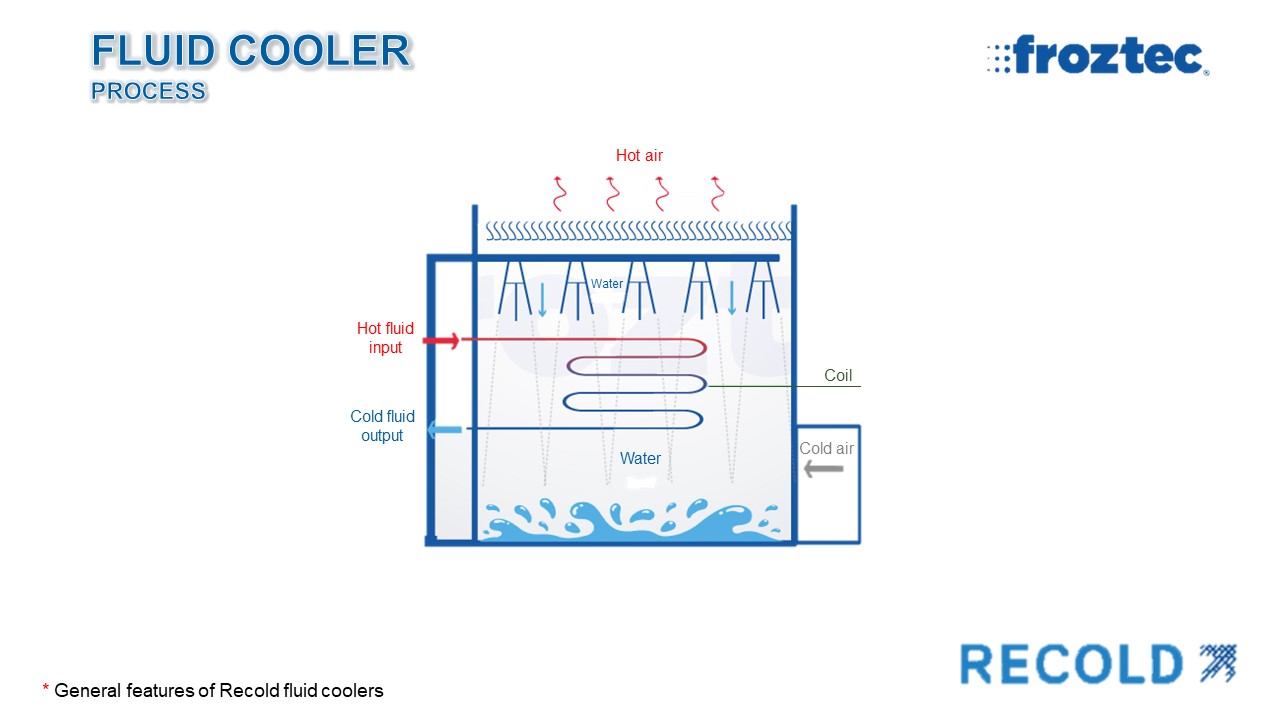
- The coil serves to pump the process fluid.
- Fresh air is forced up through the exterior of the coil while cold water is sprayed down in an efficient counterflow arrangement.
- Heat from the process fluid is transferred to the recirculating water, flowing over the
- outside of the coil tubes and reducing the temperature of this liquid.
- Hot recirculating water is pumped from the collection basin to the sprinklers.
- Water is evenly distributed over the fill media and the coil; then, a small portion of the recirculating water evaporates, efficiently rejecting heat to the atmosphere.
Basic information for a proper selection
Application, fluid to cold, required cooling capacity, water input and output temperatures, flow, city of installation, as well as dry and wet bulb temperatures.
Benefits.
- Process liquid protection against contamination
- Maximum system efficiency against soiling and encrustation
- Superior corrosion resistance
- Cost reduction in power consumption and maintenance
- Maximum space leverage in the machine rooms
- Reliable and efficient operation all year long
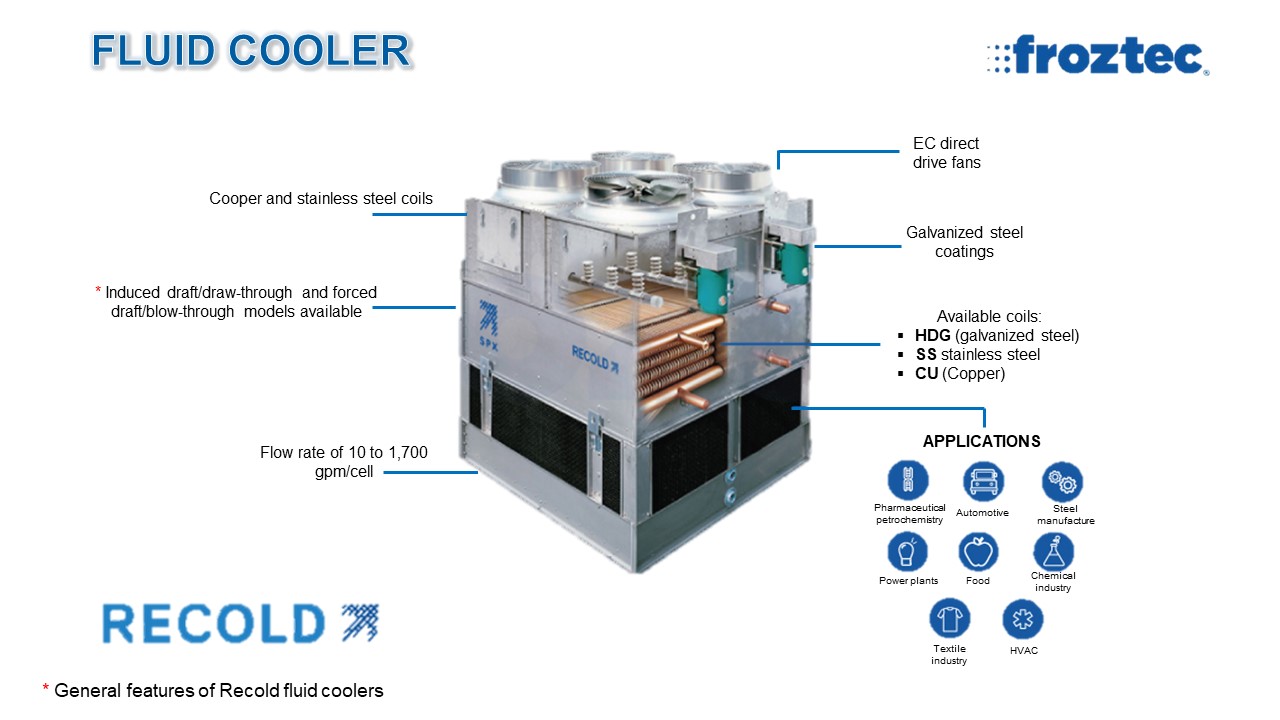
APPLICATIONS.
- Facilities climatization
- Petrochemical and Pharmaceutical industries
- Food industry
- Automotive industry
- Steel manufacture
- Electronic components manufacture
- Power plants
- Chemical industry
- Plastics industry
- Textile industry