- Home
- Infographics
- Cooling Towers
COOLING TOWERS.
What is and how does a cooling tower work?
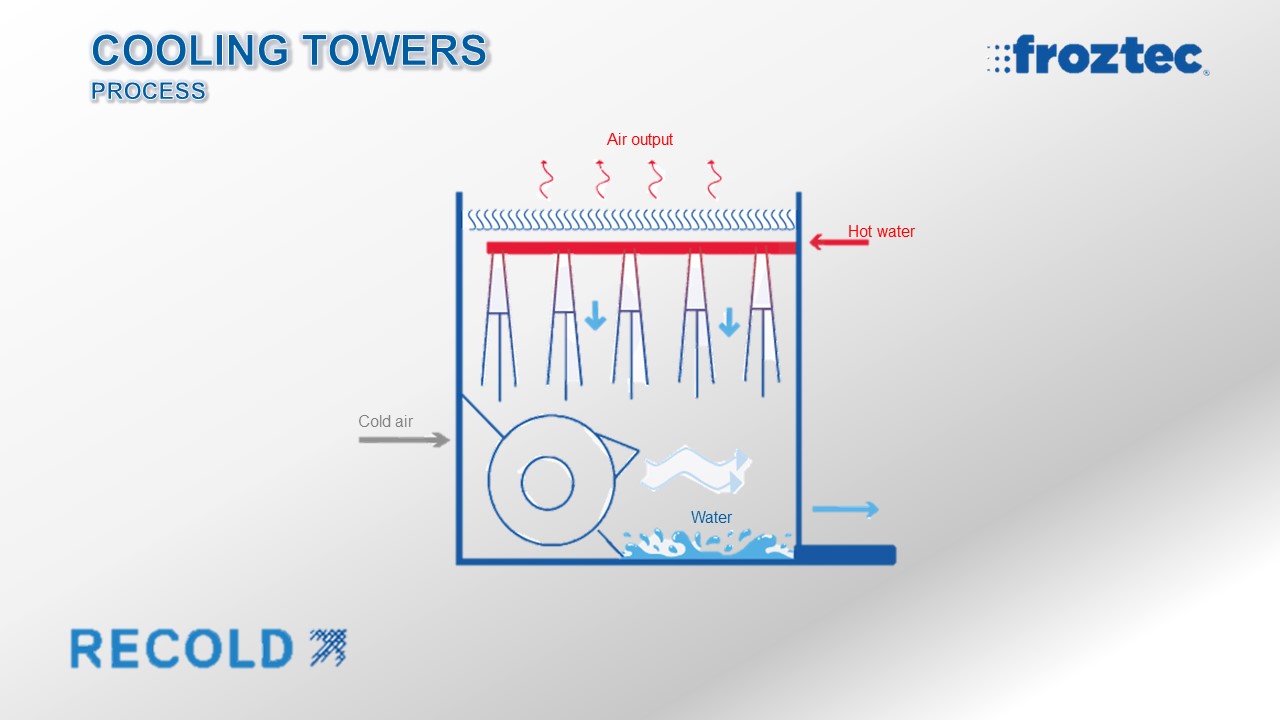
A cooling tower is a specialized heat exchanger, where air and water are brought in direct contact with each other to reduce the water temperature.Heated water during an industrial process is pumped into the cooling tower through the pipes; then, the liquid is sprayed through the nozzles onto banks of material called “fill”, which slows the water flow entering the cooling tower and exposes as much water surface as possible to achieve maximum air-water contact. As the water enters the cooling tower, it is exposed to air being pulled by the fan.
A small portion of water is evaporated once there is contact between water and air, creating a cooling action; the resulting cooled water is then pumped back to the condenser or process equipment where it absorbs heat and will then be pumped back to the cooling tower to be cooled down once again.
A small portion of water is evaporated once there is contact between water and air, creating a cooling action; the resulting cooled water is then pumped back to the condenser or process equipment where it absorbs heat and will then be pumped back to the cooling tower to be cooled down once again.
Basic information for a proper selection
Application, required refrigeration capacity, water input and output temperatures, flow, city of installation, as well as dry and wet bulb temperatures.
BENEFITS.
- More energy savings
- Less investment required than air condensers
- Lower environmental impact
- Lower acoustic impact
- Water savings
- Temperature control
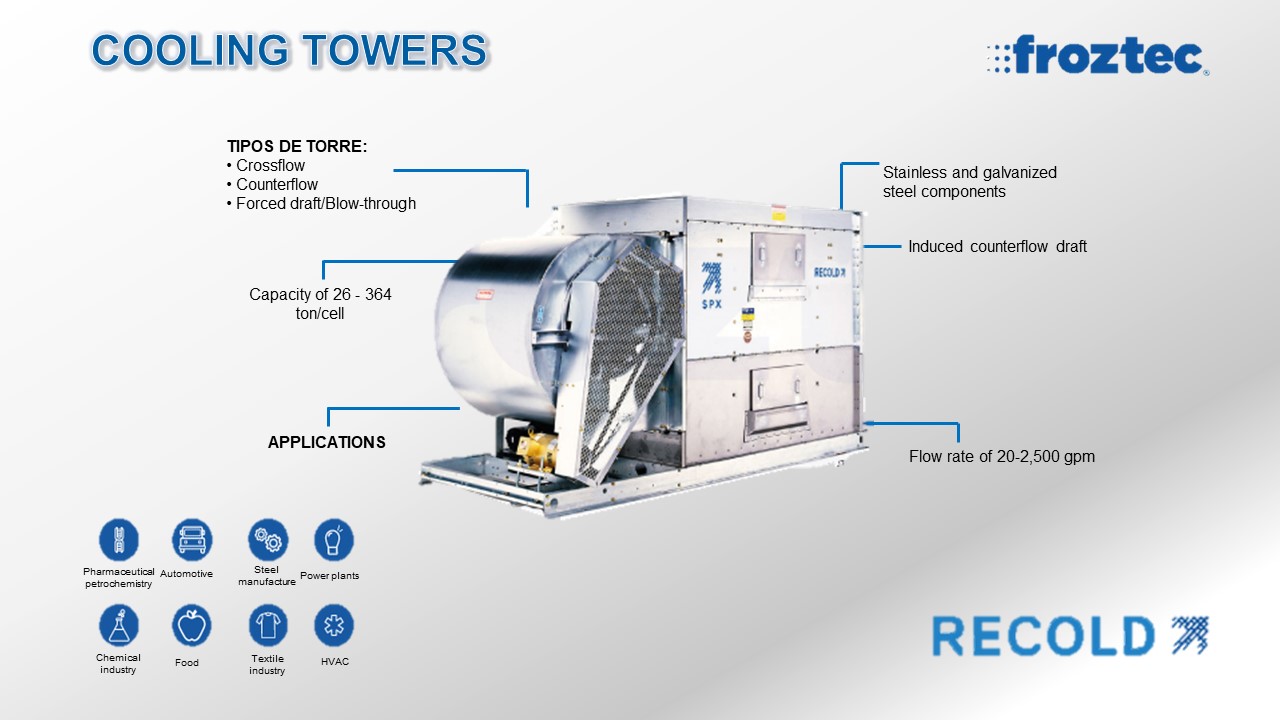
APPLICATIONS.
- Facilities climatization
- Petrochemical and Pharmaceutical industries
- Food industry
- Automotive industry
- Steel manufacture
- Electronic components manufacture
- Power plants
- Chemical industry
- Plastics industry
- Textile industry